Learn how to create PDFs with bookmarks and tags with Adobe FrameMaker.
You can customize the way PDF bookmarks and PDF tags are generated in the PDF output of a FrameMaker document or book. Use the PDF Setup dialog to configure the bookmarks and tags.
To access the PDF Setup dialog, click .
Configure bookmarks
The Bookmarks tab in the PDF Setup dialog box allows you to configure the bookmarks to include in the PDF.
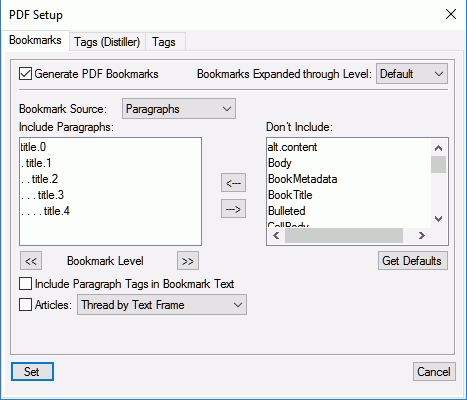
- Generate PDF Bookmarks
-
Choose to generate bookmarks in the output PDF.
- Bookmarks Expanded through Level
-
Specify the level to which the bookmarks are expanded when the PDF is opened. You can choose from the following options:
-
Select Default to open the PDF with the bookmarks expanded using the default setting of the PDF reader.
-
Select All to open the PDF with all bookmarks expanded.
-
Select None to open the PDF with all bookmarks collapsed.
-
You can also enter a number to open the PDF with bookmarks expanded to the specific level.
-
- Bookmark source
-
Select Paragraphs for FrameMaker documents and Elements for Structured FrameMaker documents.
- Bookmark Level
-
Use the double-arrow buttons below the Include Paragraphs list to increase or decrease the indentation of the bookmarks.
- Include Paragraph or Elements in Bookmark Text
-
Move paragraphs or elements between the Include and Don’t Include list to specify the paragraphs or elements to include in the bookmarks.
To move all paragraphs or elements from one list to the other, hold the Shift key and click the arrow.
- Articles
-
Set up article threading:
Thread by Text Frame: For a reading order of text frame to text frame, select Articles and select Thread by Text Frame from the drop-down list. This setting is usually the most appropriate in single-column formats.
Thread by Column: To have the reading order of each article follow the same order that the insertion point moves, select Articles and select Thread by Column from the drop-down list. This setting is usually the most appropriate in multicolumn formats.
Tagged PDF output
The tagged PDF feature creates PDF files from FrameMaker with logical document structure and extensive metadata for repurposing content. Logical structure refers to the organization of the document, such as the title page, chapters, sections, and subsections.
The default PDF generation process in FrameMaker creates tags based on the settings configured in the Tags tab of the PDF Setup dialog. If you want to use the Distiller route, then configure the structure of tags from the Tags (Distiller) tab.
Tagged PDF provides the following capabilities:
-
Ensures that information is in the correct reading order on a page
-
Includes paragraph attributes used to correctly re-flow the document contents into different-sized devices, such as eBook reading devices
-
Ensures the reliable translation of text into Unicode. This approach recognizes ligatures and hyphens, so that a Windows screen reader can correctly read all characters and words
-
Recognizes alternative text descriptions for graphics in anchored frames
-
Enables the document to be exported more reliably to Rich Text Format (RTF) and XML from Adobe Acrobat for reuse in other documents
Tagged Adobe PDF files include author content, such as pages, articles, paragraphs, tables, and graphics in anchored frames.
Tagged PDF files do not include the following information found in standard PDF files:
-
Comments, such as online notes, graphic markups, and text markups
-
Pagination artifacts, including all content that comes from master pages (such as page numbers and running headers), and any graphic objects outside anchored frames
-
Layout and typographic artifacts, such as colored bars between columns of text, horizontal lines separating footnotes from text, and table borders
-
Printing artifacts, such as crop marks, registration marks, and page information printed outside the crop marks
Use the default route to create a tagged PDF
The default route to generate PDF in FrameMaker uses a machine-learning algorithm to generate a fully compliant tagged PDF. You can also choose to manually configure tags as per the paragraph styles created in your book or document. Use the Tags tab in the PDF Setup dialog to configure the tags you want in your published PDF.
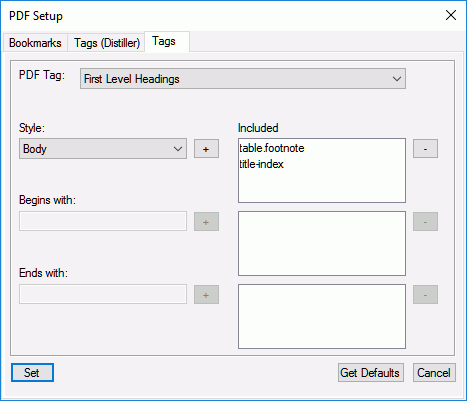
Configure the following options on the Tags tab:
- PDF Tags
-
Select an option from the PDF Tag list and map it with the corresponding paragraph Style used in your book or document.
For example, select the First Level Headings option from the PDF Tag drop-down and map it with the first-level paragraph Style used in your book or document. You can choose to specify a mapping for the first, second, and third level headings, table title, table of contents, and lists.
- Style
-
The Style drop-down list contains all styles found in your book or document.
- Begins With or Ends With
-
In case of styles that have multiple occurrences in your book, you can specify the beginning or ending characters of the style name. For example, if your table of contents style is named
TOC_abcandTOC_def, then select TOC in the PDF Tag list, and enterTOCin the Begins With field. The PDF generating engine will pick all paragraph styles beginning withTOCand assign them with the TOC tag. - Get Default
-
FrameMaker uses machine-learning algorithm to create a mapping between the tags and paragraph styles. Click on the Get Defaults button to auto-assign styles for first, second, and third-level headings. The TOC styles are simply mapped with all paragraph styles that end with
TOC. There is no mapping done for the Table Title and List tags.
Use the Distiller route to create a tagged PDF
The Tags (Distiller) tab in the PDF Setup dialog allows you to configure settings to generate a tagged PDF through the distiller route. The PDF generated through the distiller route generates a tagged PDF, but it is not a fully compliant tagged PDF.
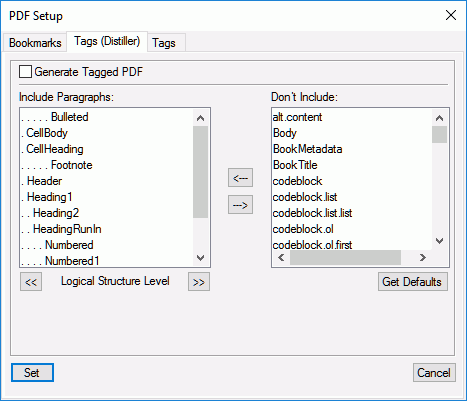
Configure the following options on the Tags (Distiller) tab:
- Generate Tagged PDF
-
Check this option to generate a tagged PDF through the distiller route.
- Include Paragraphs
-
To indicate the paragraphs to include in the PDF structure, move paragraph styles between scroll lists. The paragraphs in the Include Paragraphs scroll list are used to define the structural relationship between FrameMaker paragraph styles in the PDF file. To move a style between scroll lists, select the style and click an arrow or double-click the style.
- Logical Structure Level
-
To change structure levels for the included paragraphs, select a paragraph style and click a Logical Structure Level arrow. To change the level of all items by one level, Shift-click a Logical Structure Level arrow. If the indent for a style exceeds six levels, n> precedes the paragraph style, where n is the indentation level of the paragraph style.