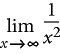A math element type indicates how the element behaves in relation to other elements around it. For example, a plus sign (+) has the type infix, which means that it has two operands, one to the left and one to the right.
You can define custom math elements of the following types.
|
Type |
Example |
Number of operands |
|---|---|---|
|
Atom |
|
None |
|
Delimiter |
|
One |
|
Function |
|
One, to the right of the element |
|
Infix |
|
Two, to the left and the right of the element |
|
Large |
|
Up to three, above, below, and to the right of the element |
|
Limit |
|
Up to two, below and to the right of the element |
|
Prefix |
|
One, to the left of the element |
|
Postfix |
|
One, to the right of the element |
|
Vertical list |
|
Two, one above the other (The text line that defines a custom vertical list is used as a separator between list items.) |
You cannot define custom math elements of the following types.
|
Type |
Example |
|---|---|
|
Derivative |
|
|
Diacritical mark |
|
|
Horizontal list |
|
|
Matrix |
|
|
Root |
|
|
Script |
|
|
Substitution |
|
|
Vertical division bar |
|