Understand how to use search in a structured XML document.
When you are working on a structured XML document, you
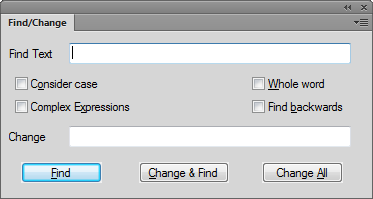
can use the FrameMaker Find/Change dialog in the WYSIWYG view.
However, if you are working the XML view, you can search Complex Expressions or XPath queries.
The XML-specific search functionalities (Complex Expression and
XPath search); perform the search in the XML content of a document.
This implies that if you are searching for content across elements
in the XML, you will need to specify the element tags in the search.
For example, the following sample paragraph (<p>)
text contains a word marked as bold (<b>).
<p>The quick <b>brown</b> fox.</p>
The WYSIWYG view provides the functionality to search for text
as it displays in the FrameMaker window. This implies that the search
for The quick brown fox will find the text. However,
in the XML view, the same search does not find any results.
In the XML view, you will need to include the <b> (opening)
and </b> closing tags in the search.
XPath queries
Understand how you can use XPath queries to navigate
through elements in an XML document in FrameMaker.
An XML document consists of a hierarchy of elements. An
XPath query is used to navigate through elements and attributes
in an XML document.
Given the following XML file:
<topic id="abc">
<title>Using XPATH</title>
<body>
<p>Using XPATH is easy.</p>
<fig>
<image href="images/xpath.png"/>
</fig>
<section>
<title>Examples</title>
<p audience="novice">A simple example.</p>
<p audience="expert">An advanced example.</p>
<p audience="expert">Another advanced example.</p>
<fig>
<image href="images/xpath-axes.png">
<alt>This screenshot shows the XPATH axes</alt>
</image>
</fig>
</section>
<p>The End.</p>
</body>
</topic>
The following table contains a list of several sample XPath queries
for the XML example given above.
XPath Query
|
Locates
|
/topic
|
Returns the <topic> root
element.
|
//title
|
Returns any <title> element.
|
//section/title
|
Returns only the <title> element
that is a child of a <section> element.
|
//p
|
Returns any <p> element.
|
//p[@audience='expert']
|
Returns any <p> element
where the @audience attribute is set to expert.
|
//p[not(@audience)]
|
Returns any <p> element
where the @audience attribute is missing.
|
//p[not(@audience='admin')]
|
Returns any <p> element
where the @audience attribute is not of value admin OR
is missing.
|
//p[text()='To start
this process']
|
Returns any <p> elements
that start with the text string To start this process.
|
//p[contains(.,'button')]
|
Returns any <p> element
that contain the text string button somewhere in
the text.
|
//image[not(alt)]
|
Returns any <image> element
that is missing the <alt> child element.
|
For more information on XPath, see http://www.w3.org/TR/xpath/
XPath toolbar
Open the XPath toolbar ().
In the XPath field, enter the query and click the Run button.
The results of the query display in the XPath Builder pod.
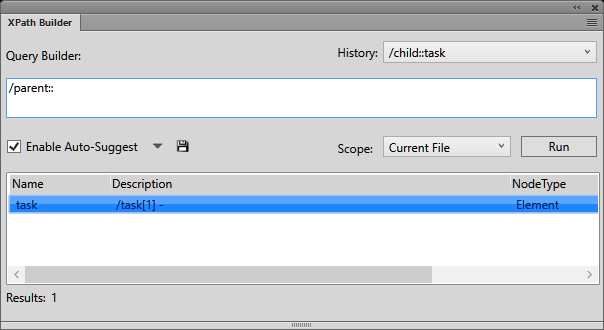
The Query Builder is also a convenient interface to build XPath
queries. In the Query Builder, you can create (using Auto-Suggest
functionality) and run an XPath query.
You can also specify the Scope of the
search:
Auto-Suggest
The Auto-Suggest feature provides suggested components
that you can add to the XPath query as you create the query.
For example, in the following XML:
<body>
<p>The quick brown fox.</p>
<p audience="admin">Jumped over the lazy dogs.</p>
</body>
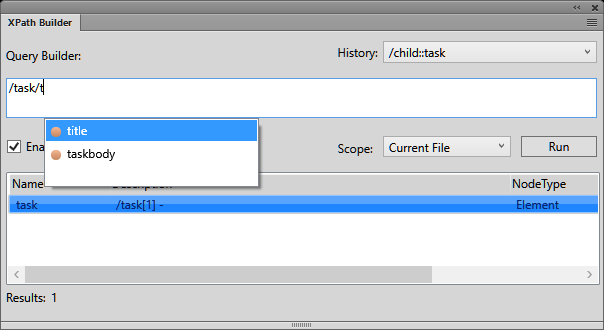
In the Query Builder field start with entering a forward
slash (/).
As soon as you enter the forward slash,
the following suggestions display:
Use the up and down arrow keys to select the option and press
Enter to insert the component into the query.
To add another element to the query, enter a forward slash.
Alternatively,
to add an attribute, enter an opening square bracket ([).
The Auto-Suggest list contains the following components of an
XPath query:
- Element (orange indicator)
Elements at the current position in the current document.
- Attribute (blue indicator)
Attributes at the current position in the current document.
- Axes (green indicator)
An axis is a node definition relative to the current node.
For example, parent, child, ancestor.
Click the drop-down
list to the right of the Enable Auto-Suggest option
and un-check the Axes option to hide the
available axes in the Auto-Suggest list.
Note: You can choose to disable the Auto-Suggest feature
in the Query Builder.
Click the Save icon to save the current
results of the XPath query.